Many swimming pools in Germany don’t have enough trained lifeguards—and in many places, this skilled labor shortage is leading to closures. The solution could be a floating underwater rescue robot.

According to one German life-saving association, nearly 420 people drowned in Germany in 2019, with the majority losing their lives in fresh water lakes, but also in swimming pools.
Now, a team of researchers from the Institute for Advanced Systems Technology of Fraunhofer Institute for Optronics, System Technologies, and Image Exploitation (IOSB) is aiming to improve the situation with an aquatic robot that uses AI, the only one of its kind worldwide.
The scientists have used their years of expertise in the area of underwater robotics to develop the autonomous device that will assist lifeguards and rescue swimmers in emergencies.
LOOK: Dad Designs a Floating Drone That Could Prevent Dozens of Potential Drownings
“There are typical postures that you can use to recognize when someone is in danger,” says computer scientist Helge Renkewitz, who led the team in close collaboration with the water rescue service, Wasserrettungsdienstes Halle e.V.
Surveillance cameras mounted on the swimming pool’s ceiling register the movement patterns and position of the drowning person in the pool, and send the coordinates to the robot. It is safely stored away from prying eyes in a docking station on the swimming pool floor, which opens in an emergency.
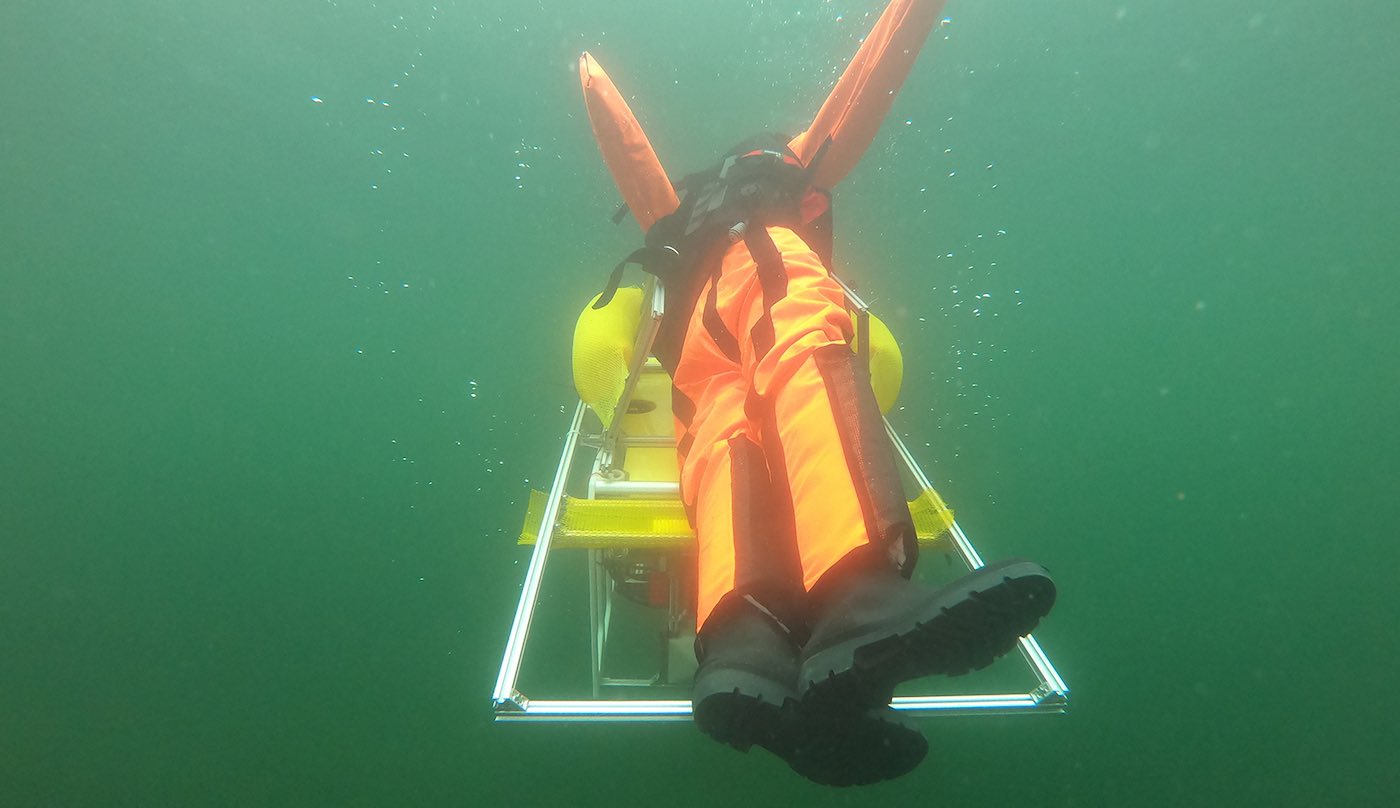
Once the vehicle has reached its destination, it locates the endangered person and carries them to the surface. A mechanism for fixing the rescuee in place prevents lifeless bodies from sliding down as they surface. This mechanism can also be mounted on other underwater vehicles.
RELATED: Lifeguards Were Just Learning to Use New Rescue Drone When They Saved Boys Trapped at Sea
Successful open-water testing
In lakes, drones and zeppelin systems take on the task of the surveillance cameras. “These drones and advertising balloons can easily be fitted with cameras,” says Renkewitz. Because the visibility is restricted, the underwater vehicle must be equipped with acoustic sensors instead of optical ones. Sound wave echoes can be used to determine people’s positions and orientation so precisely that the robot can autonomously head for the target person and pick them up.
This has been proven to work in practice through the very impressive open-water testing that researchers conducted at the Hufeisensee lake in Halle (Saale).
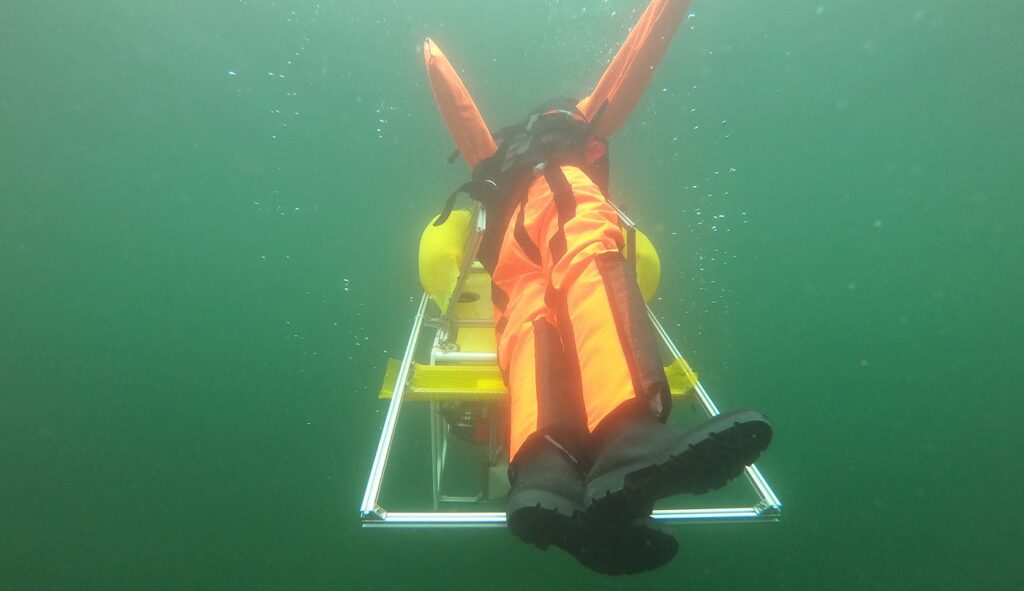

An 80-kilogram dummy was deposited at a depth of three meters. The robot then picked it up, secured it in place, brought it to the surface within a second, and carried it via the shortest route – a distance of 40 meters – to shore, where the rescue team was already waiting.
When the robot is informed of an emergency, a signal alerts the team immediately. “The full rescue operation lasted just over two minutes. Casualties must be resuscitated within five minutes to avoid long-term damages of the brain. We were able to stay within this critical time frame without any problems,” says Renkewitz.
MORE: Lifeguards in Chile Use Drones to Help Swimmers
The future outlook
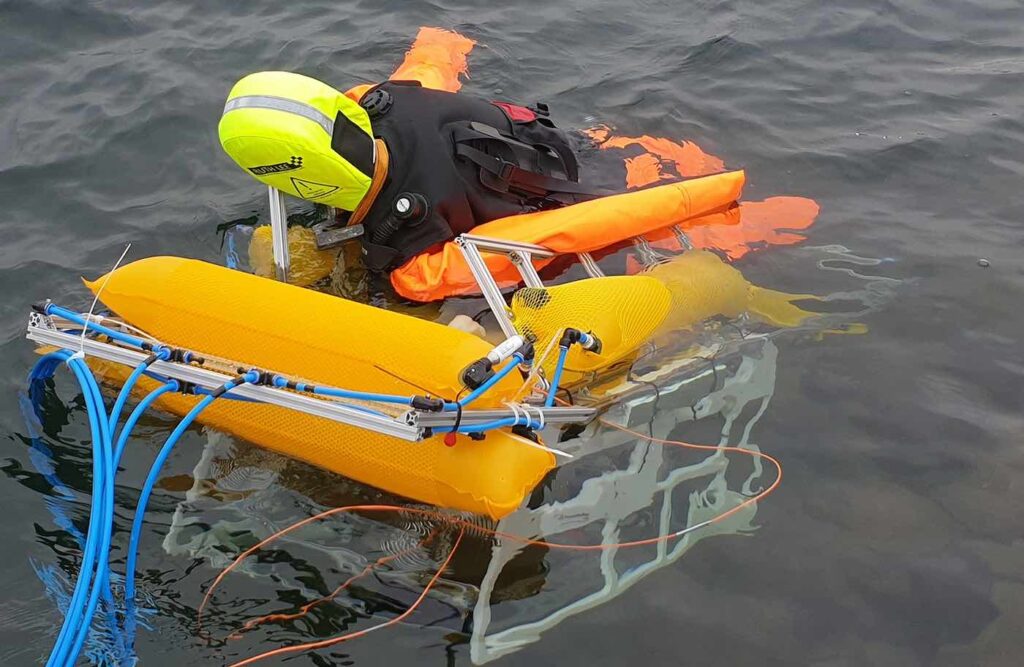
Equipped with batteries, motor, cameras, and optical and navigational sensors, the current system is 90 centimeters long, 50 centimeters high, and 50 centimeters wide. The objective of Renkewitz’s team is to further reduce the size of the rescue system and build different versions for use in swimming pools and lakes. They aim to make it smaller, lighter, and more cost-effective than the current prototype, which is based on a pre-existing underwater vehicle.
Instead, the future robot will have the streamlined design of a manta ray.
Funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy, a patent has already been filed for the aquatic robot. In modified versions, it can take on further tasks – such as offshore and dam wall inspections or being used to monitor the health of fish in fish farms.
The underwater vehicles have a very broad range of applications, such as detecting and verifying archaeological artifacts at the bottom of lakes—where fewer victims will end up, thanks to the new robot.
(Source: Fraunhofer Institute for Optronics, System Technologies and Image Exploitation)
FLOAT This Innovation Over to Your Swimming Friends on Social Media…